In the landscape of digital connectivity, where the latest technologies often
grab the spotlight, USSD (Unstructured Supplementary Service Data) is silently
and steadily making a profound impact in developing nations. This technology,
which does not rely on internet connectivity, is proving to be a crucial tool
in connecting people to a range of services that many in more developed parts
of the world take for granted. USSD gateways, with their unique ability to
provide accessible and affordable connectivity, are pivotal in empowering
communities in developing nations.
The impact of USSD is particularly noticeable in the financial sector, where it has democratized access to banking services. People can manage their finances, receive payments, and ensure their economic stability, all through a few simple commands on their phone. In healthcare, the ability to access information or communicate with medical professionals via USSD can be transformative, especially where healthcare facilities are scarce and visiting a doctor can be a day-long journey. Education, too, is being revolutionized by USSD technology. Students in remote areas can receive educational content and take quizzes through their phones. This has the potential to bridge the educational divide, providing learning opportunities to those who might otherwise be left behind.
However, the journey is not without its challenges. Infrastructure limitations can hinder the effectiveness of USSD services, and there’s a continuous need to innovate and improve the technology to meet the growing demands.
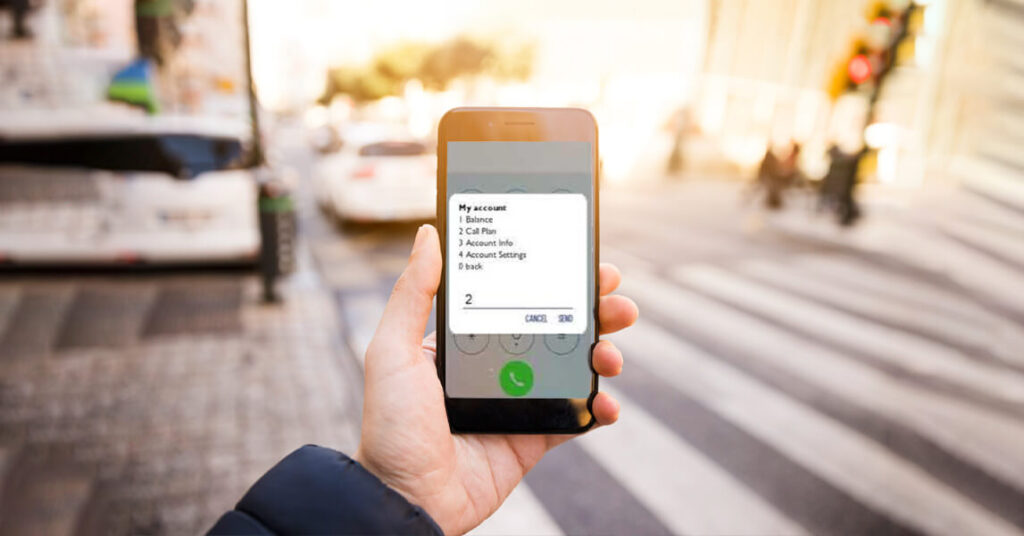
Is USSD Still Appropriate?
Imagine living in a remote village where the nearest bank or medical clinic is miles away and the internet is a rare luxury. Here, USSD technology becomes a lifeline, allowing residents to access banking services, receive medical advice, or continue their education through their mobile phones. The simplicity of USSD, requiring just a basic handset and a mobile signal, makes it accessible to the vast majority, including those who cannot afford smartphones or do not have access to stable internet connections.The impact of USSD is particularly noticeable in the financial sector, where it has democratized access to banking services. People can manage their finances, receive payments, and ensure their economic stability, all through a few simple commands on their phone. In healthcare, the ability to access information or communicate with medical professionals via USSD can be transformative, especially where healthcare facilities are scarce and visiting a doctor can be a day-long journey. Education, too, is being revolutionized by USSD technology. Students in remote areas can receive educational content and take quizzes through their phones. This has the potential to bridge the educational divide, providing learning opportunities to those who might otherwise be left behind.
However, the journey is not without its challenges. Infrastructure limitations can hinder the effectiveness of USSD services, and there’s a continuous need to innovate and improve the technology to meet the growing demands.

The Role of USSD Gateways in Developing Nations
Despite these challenges, the potential of USSD to contribute to the socio-economic development of nations is undeniable. As we move forward, it’s vital that stakeholders, from governments to technology firms, invest in and expand the use of USSD technology. By doing so, they will not only be investing in technology but in the very fabric of society, enabling individuals to connect, engage, and thrive in the digital age.As we look towards the future, USSD’s role in developing nations could evolve with the technology itself, integrating with 5G and continuing to serve as a bridge in the digital divide. Its simplicity, accessibility, and broad reach make it a powerful tool in the global quest for digital inclusion, highlighting that sometimes, the most impactful technologies are those that work quietly in the background, transforming lives one simple message at a time. Following are the key reasons why USSD plays a crucial role in developing nations: